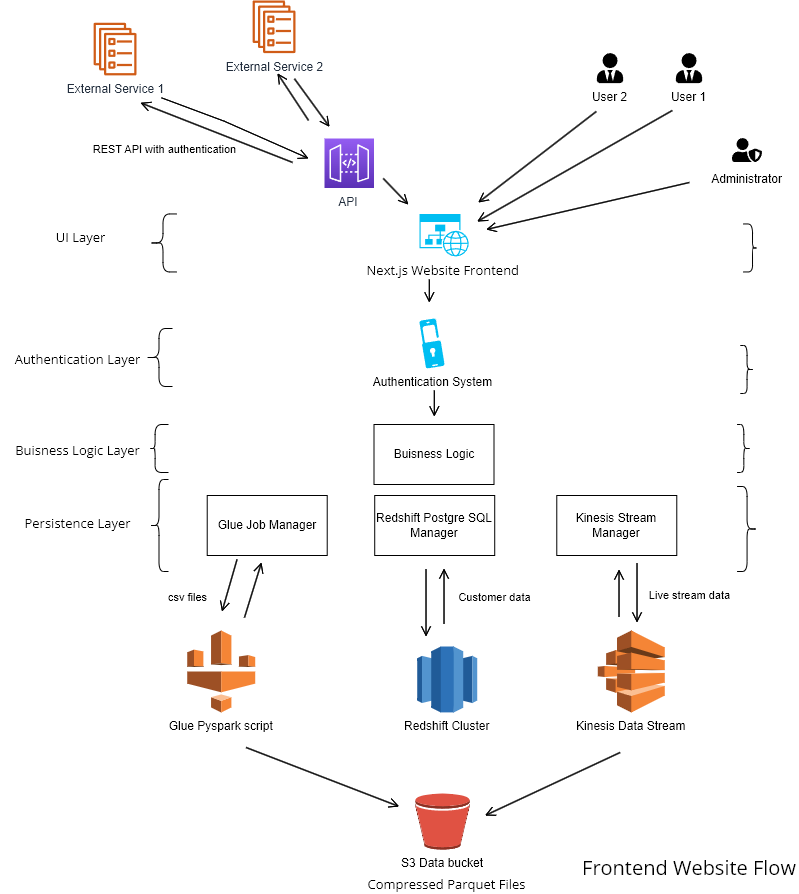
Designing a Software Architecture to Handle Petabytes of Data in AWS using Apache Spark
In today’s data-driven world, managing vast amounts of information is a common challenge. With Petabytes (PB) of data, efficient processing and storage become paramount. Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Apache Spark synergize to provide a robust solution for this challenge.
1. Foundation: AWS Infrastructure
Amazon S3: At the core of the architecture is the Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3). With its durability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, S3 serves as a reservoir for petabytes of raw data. This distributed object storage system is the primary data lake, wherein data can be stored in its native format.
Amazon EC2: Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances provide the computational power. Depending on the workloads, different types of EC2 instances can be selected. For Spark, memory-optimized or compute-optimized instances are ideal.
2. Apache Spark on AWS
Deployment: Apache Spark can be seamlessly deployed on AWS using the managed service: Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce). EMR simplifies the provisioning, configuration, and tuning of Spark clusters, thus facilitating scalability and fault-tolerance.
Processing: Spark’s in-memory processing capabilities significantly speed up big data workloads, especially iterative algorithms. This in-memory computation is particularly useful for processing petabytes of data, as it minimizes the read-write operations to disk, thereby accelerating tasks.
Data Frames & SQL: Spark’s DataFrames API provides optimizations through Catalyst and Tungsten engines. Users can also run Spark SQL on data stored in S3, offering a versatile approach to querying large datasets.
3. Data Ingestion
AWS Data Migration Service & Kinesis: For continuously generated data, Amazon Kinesis captures, processes, and stores streaming data. Meanwhile, AWS Data Migration Service is excellent for one-time migrations or ongoing replications.
Direct S3 Uploads: Data can also be directly uploaded to S3 using the Multipart Upload API for large datasets, ensuring both speed and resiliency.
4. Data Optimization & Lake House Architecture
Data Formats: Transforming data into columnar formats like Parquet or ORC helps in efficient querying. These formats are optimized for analytics on big data platforms like Spark.
Databricks Delta Lake: To provide ACID transactions, schema enforcement, and time travel capabilities, Delta Lake on Databricks can be used on top of the S3 data lake. This creates a ‘Lake House’ architecture that unifies the best of data lakes and data warehouses.
5. Scalability & Resilience
Auto-Scaling with EMR: EMR clusters can be configured to auto-scale based on workload, ensuring resources are used optimally.
Spot Instances: To cost-effectively scale Spark jobs, AWS Spot Instances can be utilized with EMR. These offer significant cost savings but may be reclaimed if the spot price exceeds the bid. However, EMR manages this by checkpointing Spark jobs and moving tasks to on-demand instances if required.
6. Security & Compliance
Data Encryption: With Amazon S3 server-side encryption (SSE), data at rest is secured. Data in transit can be secured using SSL/TLS.
IAM & VPC: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) ensures fine-grained access control. Additionally, running Spark clusters within Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) isolates the environment, enhancing security.
7. Monitoring & Optimization
Amazon CloudWatch & Ganglia: For monitoring Spark clusters, CloudWatch offers metrics, while Ganglia provides in-depth cluster insights.
AWS Glue: AWS Glue’s Data Catalog is an excellent solution for metadata storage, making it easier to discover and manage data.
In conclusion, when handling petabytes of data, AWS’s vast ecosystem combined with Apache Spark’s processing prowess forms a scalable, resilient, and cost-effective architecture. Proper planning and leveraging the right AWS services will ensure smooth processing, storage, and management of massive datasets.